Key Event: Historic Visit of the British Prime Minister
In October 2025, British Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s visit to India marked a new chapter in bilateral relations. During the two-day visit, India and the UK signed several key agreements that will shape the trajectory of relations over the coming decade.
Historic Cooperation in the Defense Sector
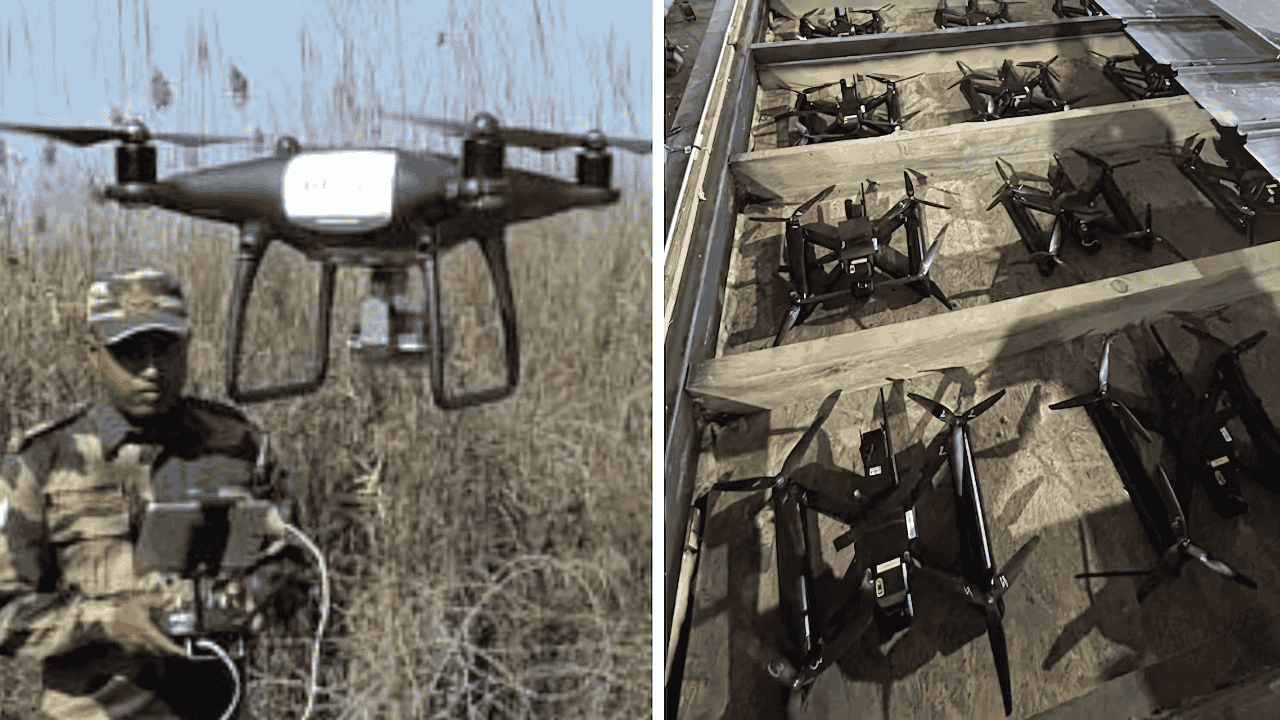
₹4200 Crore Missile Deal
The most significant agreement was a missile deal worth £350 million (about ₹4200 crore). Under this agreement:
India will procure Lightweight Multirole Missiles (LMMs) for its armed forces
These missiles will be manufactured by Thales Company in Belfast, Northern Ireland
The deal is expected to create 700 jobs in the UK
These are the same missiles currently being produced for Ukraine
Other Defense Cooperation
Indian Air Force flying instructors will now serve as trainers in the Royal Air Force (RAF), UK
An initial agreement worth £250 million has been signed for the development of electric engines for the navy
Revolutionary Cooperation in Higher Education
9 British Universities Opening Campuses in India
Prime Minister Modi announced that 9 British universities will set up campuses in India:
Already established/approved campuses:
University of Southampton – Gurugram (already operational)
University of Liverpool – Bengaluru
University of York – Mumbai
University of Aberdeen – Mumbai
University of Bristol – Mumbai
Lancaster University – Bengaluru
University of Surrey – GIFT City, Gujarat
👉 This represents the largest higher education footprint of any foreign country in India.
Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement
Status of the Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
The India–UK Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA), signed in July 2025, is expected to be implemented within a year.
Key Features:
99% of Indian exports will get zero-duty access
Tariffs will be reduced on 90% of UK exports
Target: $120 billion bilateral trade by 2030
UK Investment Announcements
During Starmer’s visit, 64 Indian companies announced £1.3 billion investment in the UK, expected to create 6,900 new jobs.
Visa and Migration Issues
Work Visa for Indian Professionals:
Currently, 82,000 Indian professionals receive UK work visas annually. India has demanded an increase to 125,000 per year.
Student Visa Quota:
India is also pushing to raise the annual quota from the current 92,000 students.
Young Professionals Scheme:
For 2025, 3,000 slots have been reserved for Indian citizens aged 18–30, allowing them to live and work in the UK for up to two years.
Technology and Innovation
Critical Minerals Observatory
A satellite campus of the UK–India Critical Minerals Supply Chain Observatory will be set up at IIT-ISM Dhanbad.
Objectives:
Ensuring a secure supply chain of critical minerals
Promoting green technologies
Advancing mining sector research and innovation
FinTech Cooperation
Establishment of the UK–India FinTech Corridor to:
Provide opportunities for startups to pilot and scale innovations
Enhance cooperation between the London Stock Exchange and GIFT City
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
PM Modi announced that while the AI Safety Summit began in the UK, the AI Impact Summit will be hosted in India next year.
For India, AI stands for “All Inclusive.”
Political and Diplomatic Issues
Khalistan Issue
PM Modi raised concerns about Khalistani elements active in the UK:
Violence and extremism have no place in democracy
Action must be taken under the legal frameworks of both countries
Democratic freedoms should not be misused
India’s Economic Prospects
Third-Largest Economy by 2028
According to Morgan Stanley, India will become the world’s third-largest economy by 2028, surpassing Germany.
Key Projections:
GDP by 2028: $5.7 trillion
GDP by 2035: $10.6 trillion (double of 2028)
Contribution to global growth in the next decade: 20%
Vision 2035 Roadmap
Both countries adopted a 10-year roadmap under Vision 2035 covering:
Trade and investment
Technology and innovation
Defense and security
Climate and energy
Health and education
People-to-people ties
Importance for Exam Preparation
For UPSC Mains
International Relations (GS Paper-II):
Evolution of India–UK bilateral relations
Impact of Free Trade Agreements
Strategic significance of defense cooperation
Diplomatic challenges of the Khalistan issue
Economy (GS Paper-III):
Economic impact of FTA and trade balance
India’s improving global economic position
Strategic importance of critical minerals
International cooperation in the FinTech sector
Science & Technology (GS Paper-III):
Cooperation in defense technology
India–UK partnership in AI
Expansion of Digital Public Infrastructure globally
Possible Mains Questions
“How important is the India–UK Free Trade Agreement for India’s economic diplomacy? Evaluate its potential advantages and challenges.”
“Why is a secure supply of critical minerals essential for India’s energy security?”
“How is India’s FinTech revolution enhancing its soft power in the age of digital diplomacy?”
Key Facts for Prelims
LMM Missile Deal: £350 million
9 British universities opening campuses in India
Critical Minerals Observatory at IIT-ISM Dhanbad
India to become third-largest economy by 2028
Adoption of Vision 2035 Roadmap