Hoysala Empire: The Golden Chapter of South Indian Art
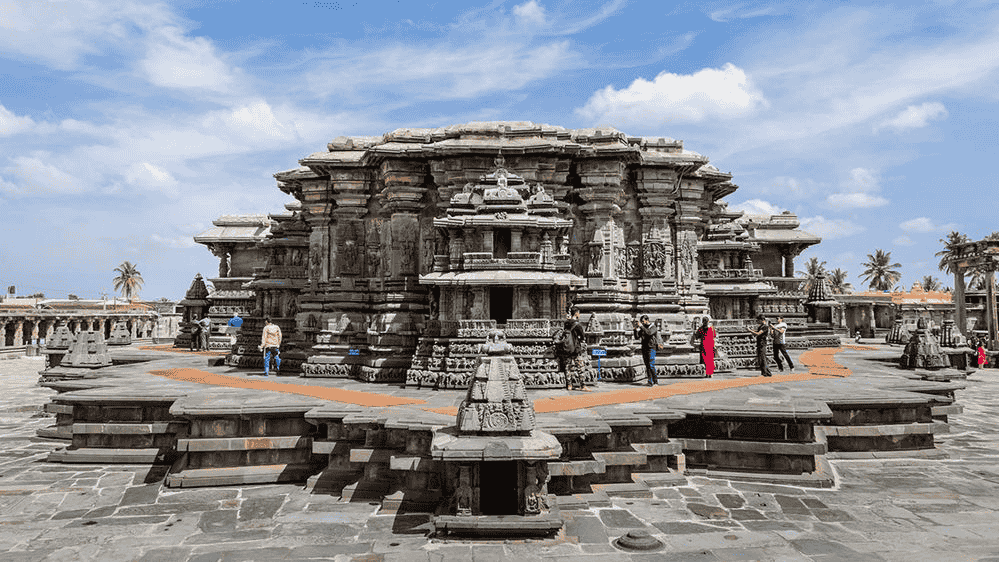
The Hoysala Empire (11th–14th century) was a powerful dynasty in Karnataka that made invaluable contributions to Indian temple architecture. In September 2023, Hoysala temples were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, bringing India’s total UNESCO sites to 42.
Key Features of Hoysala Temples
Architectural Structure:
Temples built on stellate (star-shaped) plans
Use of soapstone, which allowed for fine and intricate carvings
Medium-height vimanas and complex mantapa (halls)
Circumambulatory path with sculptural galleries
Artistic Excellence:
Hyper-realistic sculptures and stone carvings on the walls
Lifelike depictions of deities, dancers, and musicians
Scenes from the Ramayana, Mahabharata, and Bhagavata Purana
Over 240 wall sculptures in the Halebidu temple
UNESCO-Recognized Main Temples
Chennakeshava Temple, Belur
Construction Period: 1117–1220 CE (completed in 103 years)
Built by King Vishnuvardhana to commemorate victory over the Cholas
Contains 118 inscriptions from the 12th–18th centuries
Hoysaleswara Temple, Halebidu
Built in 1121 CE during the reign of King Vishnuvardhana
A twin sanctum (dwi-garbhagriha) temple dedicated to Lord Shiva
Sponsored by merchants and wealthy citizens
Kesava Temple, Somanathapura
Constructed in 1268 CE during the reign of Narasimha III
A Trikuta (triple-shrine) temple dedicated to Janardana, Kesava, and Venugopala
Built by Somnath Dandanayaka
Evolution of Hoysala Architecture
Early Phase (before the mid-12th century):
Strong influence of Western Chalukya style
Basic Dravidian morphology
Post-independence phase (after mid-12th century):
Influence of Bhumija style (Central India)
Integration of Nagara traditions (North and West India)
Development of Karnataka Dravida mode
Recognition of Hoysala craftsmen for original innovations
Other Notable Hoysala Sites
Belavadi (1200 CE)
Amritapura (1196 CE)
Hosaholalu
Arasikere (1220 CE)
Basaralu
Kikkeri
Nuggihalli (1246 CE)
UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Karnataka
With the inclusion of Hoysala temples, Karnataka now has 4 UNESCO sites:
Cultural Heritage Sites:
Hoysala temple group (2023)
Group of Monuments at Hampi (1986)
Group of Monuments at Pattadakal (1987)
Natural Heritage Site:
4. Western Ghats (2012)
Conservation and Management of Hoysala Temples
Being protected monuments under the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), these temples enjoy complete legal protection. Following UNESCO recognition:
Rise in international tourism expected
Financial assistance and expert guidance from the World Heritage Committee
Enhanced global recognition and cultural validation
Current UNESCO Tentative Sites in India
India’s UNESCO tentative list includes 50 sites, such as:
Mudumal menhirs (Telangana)
Kanger Valley National Park (Chhattisgarh)
Why This Matters for Your Exam Preparation
For UPSC Prelims:
Art & Culture (GS Paper-I):
Unique features of Hoysala architecture and comparison with other South Indian styles
Classification under Vesara or Chalukyan architectural style
Updated list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites and Karnataka’s contribution
Current Affairs Connection:
Important 2023 achievement – India’s 42nd UNESCO site
Linkages with cultural nationalism and heritage conservation policies
Implications for tourism and economy
For UPSC Mains:
Comparative Analysis: Hoysala vs Chola vs Pallava architecture
Cultural Continuity: Evolution of medieval South Indian art traditions
Heritage Management: Impact of UNESCO recognition on conservation and tourism
Previous Year Questions (PYQs):
In UPSC Prelims 2024, a direct question was asked on UNESCO World Heritage Sites
Questions on the Hoysala dynasty are frequently repeated