Raja Ram Mohan Roy’s 253rd Birth Anniversary: Key Facts and Exam-Relevant Information
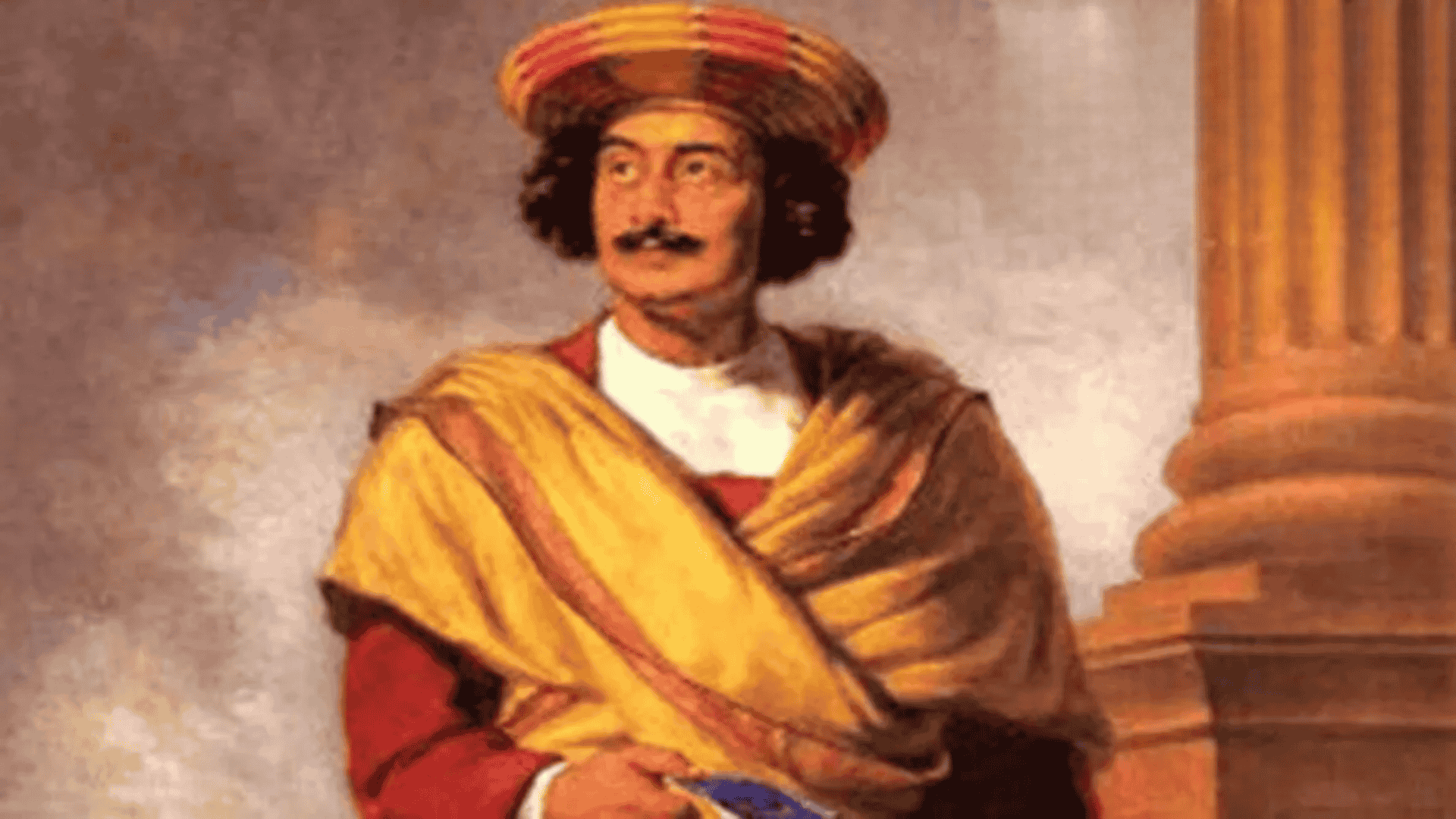
Raja Ram Mohan Roy, often called the “Father of Modern India,” was born on 22 May 1772 in Radhanagar village, West Bengal, into a distinguished Brahmin family. On the occasion of his 253rd birth anniversary this week, it is essential for aspirants preparing for UPSC and other competitive exams to know about his contributions.
Raja Ram Mohan Roy: Pioneer of Modern Indian Thought
Birth: 22 May 1772, Radhanagar, West Bengal, in a prominent Brahmin family
Known as: Father of Modern India; key architect of the Indian Renaissance
Belief: Advocate of scientific and modern education for societal progress
Major Contributions and Exam-Relevant Facts
1. Initiation of English Writing in India
In 1809, Raja Ram Mohan Roy became the first Indian to write directly to the British Governor-General Lord Minto in English.
This marked the beginning of ‘Indian Writing in English’.
He wrote several articles in English on social and religious issues and encouraged Indians to adopt the English language and Western thinking.
2. Advocacy for Modern Education
When a British officer claimed that Indians were not fit for democracy or modern education, Ram Mohan Roy argued that Indians should receive good and modern education so they could understand their rights and duties.
He believed education should not be limited to bookish knowledge, but should also promote scientific thinking, human rights, rationality, and modern values.
3. Abolition of Sati
Due to his active efforts, the British government officially banned the practice of Sati in 1829.
This was a historic social reform and a significant step towards women’s rights.
4. Founding of Brahmo Samaj (1828)
Founded the Brahmo Samaj in 1828, which became a center for social and religious reform.
The Brahmo Samaj promoted rationality, social equality, and opposition to orthodox practices.
5. Title of ‘Raja’ and Diplomatic Role
Mughal Emperor Akbar II sent Ram Mohan Roy to England in 1830 to advocate for the emperor’s pension and rights before the British government.
Impressed by his intellect and communication skills, Akbar II conferred upon him the title of ‘Raja’.
6. Promotion of English and Modern Education
Played a significant role in starting English-medium schools and colleges.
Collaborated with David Hare and Reverend Adam in establishing Hindu College (later Presidency College), English High School (1822), and Vedanta College (1826).
He believed education should inspire thinking, questioning, and social reform.
Key Facts for Exams
Born: 22 May 1772, Radhanagar, West Bengal
Founded: Brahmo Samaj (1828)
Major Reform: Abolition of Sati (1829)
Diplomatic Mission: Sent to England by Akbar II (1830)
Title: ‘Raja’ (conferred by Mughal Emperor Akbar II)
Educational Initiatives: Hindu College, English High School, Vedanta College
Related Articles on Atharva Examwise
Important Social Reformers in Modern India – UPSC Notes
Top 10 Current Affairs May 2025 – Daily GK Update
Read All Current Affairs at Atharva Examwise
Why this matters for your exam preparation
History & Modern India:
Raja Ram Mohan Roy’s reforms are crucial for UPSC Prelims and Mains, especially for Modern Indian History, social reform movements, and key personalities.
GS Paper 1 & Essay:
His advocacy for modern education, women’s rights, and rationalism are frequently referenced in essay and GS answers.
Ethics & Society:
His life exemplifies ethical leadership, rational thinking, and social responsibility, which are important for GS Paper 4.
Current Affairs Connection:
His legacy is often cited in contemporary issues related to education, women’s rights, and social reforms.
Tip:
Make concise notes on Raja Ram Mohan Roy’s reforms, educational initiatives, abolition of Sati, and the role of Brahmo Samaj. Link these facts to static topics in history and society for value-added answers in Prelims and Mains.
For more exam-focused news and analysis, stay updated with Atharva Examwise Current Affairs.